This year Egypt tops the list of reformers that are making it easier to do business. Egypt's reforms went deep with reforms in 5 of the 10 areas studied by Doing Business, and it greatly improved its position in the global rankings as a result. Besides Egypt, the other top 10 reformers are, in order, Croatia, Ghana, FYR Macedonia, Georgia, Colombia, Saudi Arabia, Kenya, China, and Bulgaria.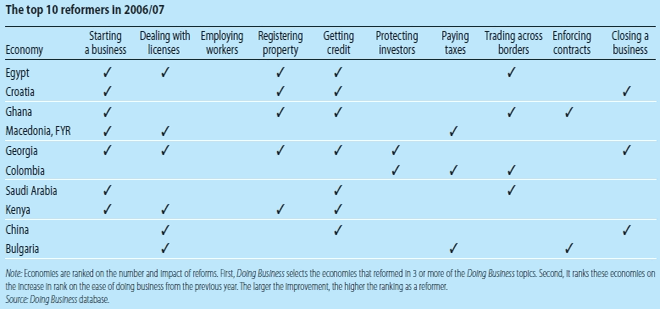
Here is a brief summary of some of the key reforms that took place:
Egypt, the top reformer in the region and worldwide, greatly improved its position in the global rankings on the ease of doing business. Its reforms went deep. Egypt cut the minimum capital required to start a business, from 50,000 Egyptian pounds to just 1,000 and halved the time and cost of start-up. It reduced fees for registering property from 3 percent of the property value to a low, fixed amount. It eased the bureaucracy that builders face in getting construction permits. It launched new one-stop shops for traders at Egyptian ports, cutting the time to import by seven days and the time to export by five. And it established a new private credit bureau that will soon be making it easier for borrowers to get credit.
Croatia reformed in four of the 10 areas studied by Doing Business. Two years ago, registering property in Croatia took 956 days. Now it takes 174. Company start-up also became faster, with procedures consolidated at a “one-stop shop” and pension and health services registration now online. Credit became easier to access: a new credit bureau was launched, and a unified registry now records charges against movable property in one place. In its first two months, €1.4 billion in credit was registered. In addition, amendments to the country’s insolvency law introduced professional requirements for bankruptcy trustees and shorter timelines.
Ghana, a top 10 reformer for the second year running, continues to increase the efficiency of its public services. It cut bottlenecks in property registration, reducing delays from six months to one. Greater efficiency at the company registry and the environment agency cut the time for business start-up to 42 days. Changes in the port authority’s operations sped up imports. New civil procedure rules and mandatory arbitration and mediation reduced the time it takes to enforce contracts.
FYR Macedonia eliminated the minimum capital requirement for business start-up, sped up the process for getting construction permits, lowered the corporate income tax rate to 12 percent (with another cut to 10 percent planned for 2008), and simplified tax payment procedures. Its ranking on the ease of doing business rose from 96 to 75.
Georgia reformed in six areas. It strengthened investor protections, including through amendments to its securities law that eliminate loopholes that had allowed corporate insiders to expropriate minority investors. It adopted a new insolvency law that shortens timelines for reorganization of a distressed company or disposition of a debtor’s assets. Georgia sped up approvals for construction permits and simplified procedures for registering property. It made starting a business easier by eliminating the paid-in capital requirement. In addition, the country’s private credit bureau added payment information from retailers, utilities, and trade creditors to the data it collects and distributes.
Colombia, the region’s top reformer, has made great strides in easing trade. By extending port operating hours and adopting more selective customs inspections, it reduced the time for port and terminal handling activities by three days. The country strengthened investor protections by increasing disclosure requirements for related-party transactions. It introduced an electronic tax filing system, cutting the average time businesses must spend on tax compliance each year by 188 hours, or 41 percent. And it is progressively reducing the corporate income tax rate, from 35 to 34 percent in 2007 and 33 percent in 2008.
Saudi Arabia, the runner-up reformer in the region, eliminated the minimum capital requirement of 1,057 percent of income per capita and reduced the days needed for company start-up from 39 to 15. It launched a commercial credit bureau whose reports include the credit exposure of companies. It also sped up trade, reducing the number of documents required for importing and cutting the time needed for handling at ports and terminals by two days for both imports and exports.
Kenya, the region’s other top 10 reformer, launched an ambitious licensing reform program. So far the program has eliminated 110 business licenses and simplified eight others. The changes have streamlined business start-up and cut both the time and cost of getting building permits. The program will eventually eliminate or simplify at least 900 more of the country’s 1,300 licenses. Property registration is also faster now, thanks to the introduction of competition among land valuers. And the country’s private credit bureau now collects a wider range of data.
In China, a new property law put private property rights on equal footing with state property rights. The law also expanded the range of assets that can be used as collateral to include inventory and accounts receivable. The new bankruptcy law gives secured creditors priority to the proceeds from their collateral. Construction also became easier, with electronic processing of building permits reducing delays by two weeks.
Bulgaria eased the tax burden on businesses and made it easier to pay taxes online. Bulgaria also introduced private bailiffs to improve efficiency in enforcing judgments. And it made building inspections less burdensome.
